I realized that either at work or while surfing the internet; I come across something trending or something I never knew about in the tech-industry. I curiously read about it or use it if needed and then move on and unfortunately forget it over time.
Finally, I decided to create a space where I journal my learnings, as frequently as possible. This “Today I learned” series is a very raw brain-dump write-up (no glorification, please!) of these learnings, largely to ensure that I record things that I come across.
Because this might have tons of stuff from different sub sections of Computer Programming, I might sort them out later and organize categories better - One Day!

Class Templates in C++ November 5, 2022
After a long hiatus from journaling my work, here I am documenting more of the work I learn.
TIL that while function templates do not support default arguments in the signature, class templates do!! (how cool is that?!). Class templates support default arguments for the type or non-type arguments.
For example, this below is absolutely valid.
template <class T, int SIZE = 1000>
class BigArray {
...
}
So BigArray<double> big_array_object essentially means BigArray<double, 1000> big_array_object when the compiler instantiates the class template. And as default args go, you can manually specify the variable too if you want.
And similar default parameter could be the data type for the class template.
template <class T = double, int SIZE = 5000>
class BigArray {
...
}
So BigArray<> double_array is a BigArray for double type of size 5000. Not using the <> angle brackets results in a compiler error.
Unions in C++ April 18, 2021
A union is a special class type in C++, defined similar to a class or a struct but can hold only one of its non-static data types at one time. The last written member variable is the only active variable of the union and accessing other variables results in undefined behavior. The memory held by a union is the size of its largest data type and all other variables and stored within the same memory location when active.
Type Punning in C++ April 8, 2021
While type casting is a standard technique to convert one data type to another, type punning is the paradigm of handling the contents of a memory addresss circumventing the data type limitations. It is when data as one data type and retrieved as another. It is usually done to store data in memory as any standard data type and read as a sequence of raw bytes/bits for either transport or raw copy or conversion to another similar data type.
Decorators in Python March 9, 2021
Python allows defining a method inside a method. Decorators in Python allow wrapping a method with an additional method adding some functionality on top. It maybe called a callable that returns a callable. Decorates are helpful in changing the behavior and avoid redudancy.
Application Binary Interface - ABI March 8, 2021
ABI or application binary interface is one of the most low-level elements defining the interactions between libraries, programs, and the operating system. ABI is the interface between any two binaries, either executables or libraries after compilation. ABI defines the interaction methodologies and underlying ALU manipulation and memory management that facilitates the interaction.
The interface defines how all parts of the code behave as machine code and interact with the hardware elements like registers, DRAM, and memory.
API or application program interface is a standard term used in the SW development industry. It is responsible for defining how, at the highest level, can a piece of code be interacted with. It defines the public functions, constants, data structures and more from the package can be used to integrate with the library. The ABI is the lower-level version of the API. It defines the behavioral elements of the compiled code and how it uses registers, stacks and the other hardware resources. The ABI is responsible for defining everything about an external library that the application needs. It is important the different independently-compiled code elements share the same ABI else they become incompatible. Since Windows and Linux used different ABIs, programs compiled on one cannot be used on the other.
Name Mangling February 3, 2021
The compiler has to encounter names of functions, classes or structs over different files, folders, libraries and contexts under the same project. Name mangling is the process of encoding the names/identifiers with extra information for uniqueness and identification. The need for adding identifiers with additional information comes from supporting features like namespaces and function overloading where the same identifier could behave differently, in languages like C++. The compiler hands over this semantic information to the linker to provide the complete identity of the code elements to generate the object code.
There is much more about this, which I don’t want to write here!
ldd December 22, 2021
List Dynamic Dependencies (LDD) is a command-line utility in Linux/Unix to discover the list of shared libraries required by another library/program. It is mainly used to print if a shared dependency is missing or has a broken link. Dynamic libraries help avoid compilation overhead of the dependencies, while compiling the main program.
ldd /path/to/executable/programdisplays the shared library dependenciesldd -v /path/to/executable/programadds more verbose description- Additional tags like
-uandrare used to print the unused direct dependencies and used on dynamic executables respectively
-fPIC tag in gcc/g++ November 27, 2020
-fPIC is a tag, used as a flag for CMake or any other meta build system meant to determine position independence in the machine code. If fPIC is turned on, it ensures that code execution is independent of the address the machine-generated code resides in, when the code execution jumps from one address to another.
When a shared library is created and shared with multiple applications, it is not certain if the code is loaded into the same memory address always. Thus, fPIC needs to be ON to ensure proper functioning of the code. For static libraries, runtime relocation is not needed and thus works without fPIC flag.
Amazing StackOverflow link for more details.
CCache in C++ November 26, 2020
It is a compiler cache that caches (locally stores) the previous builds for reuse during the next compilation. It helps speed up clean compilation efforts. It supports common compilers like GCC and Clang and common OSes including Linux, Windows and macOS. It is limited to only single-file caches and multi-file compilation and linking falls back to the actual compiler.
Virtual Destructors in C++ February 22, 2020
When a pointer to the base class is used for a derived class object, during the deletion of the object there could be undefined behavior if the base class destructor is NOT virtual. In order to correctly delete the base class as well as the derived class, the base class destructor is defined as virtual. Else, when the pointer to the base class is deleted, only the base class destructor is called while the derived class remains in a bad state causing memory leaks.
The corrrect process of object deletion is to call the destructors in reverse order, i.e. - from the last derived class (which the object actually belongs to in the hierarchy) to the base class.
Note: Often, there could be a pure virtual destructor and such destructors need to have a body to be acceptable.
semaphores in C++ January 12, 2020
Synchronization features like mutexes/locks and semaphores are kernel level features. A semaphore is a counting and signalling mechanism. It informs threads if a resource it is seeking, that was previously unavailable is now available or not. When multiple items are being managed, a semaphore can have a maximum count value that limits how many signals will to catered to.
Waiting on a semaphore reduces the count, not beyond zero and signalling one increases the count, not beyond the maximum.
Good Read: Multi-Threading
dmesg January 2, 2020
While I have been using for a little over 4 years now, I still can’t the depth of its tools, techniques and uses. dmesg is one such tool that prints out the message buffer of the kernel which usually has the data from device managers/drivers.
The command dmesg helps maintain a log of messages from device drivers, which may roll away quickly during boot or be supressed during some other activity. It helps track messages regarding compatibility, functionality and more.
condition variable in C++ January 9, 2020
C++ is a very efficient language that supports highly flexible and robust multi-threading procedures. C++ provides condition variable, an object that is capable of blocking the callee thread for pre-defined time period or online event.
The condition variable acquires a unique_lock on the thread and it can only be unlocked when the notification method is called on it from another thread.
std::condition_variable cv; // Declaration
cv.wait(thread); // Lock the thread
cv.notify_all(); // Release the lock
single responsibility principle January 1, 2020
Writing clean, extensible, legible and flexible code is quite a challenging task. Collaborative coding is even more difficult and several computer programming principles urge developers to KISS (keep it simple stupid!).
In a similar approach, the single responsibility princple suggests designing modules, functions and classes with only one responsibility or behavior. While this may result in bloating the code base and files, it maintains a highly modular and very extensible code base.
The function/method implementation should reflect its name and it should implement no more.
For example, a function computeSurfaceArea() should only compute the surface area of a sphere not be updating the cost of painting it as an additional step, even if it is the next logical step. The step of updating the cost should be explicity made where the code really wants it to be done and not hidden. This shall avoid issues with tracking flow of execution and instructions while debugging.
vtables in C++ December 14, 2019
One of the most useful aspects of OOP is polymorphism and allows for inheritance structure to relate functions between the base and derived classes as desired.
In a hierarchy with no virtual functions, functions are linked to the classes and all its objects at compilation via static dispatch. If there are virtual classes in the hierarchy; the compiler does not know, at compile time, to correctly associate function definitions with objects or classes. It only knows that they might or might not be overridden in derived classes.
By dynamic dispatch, the compiler is able to correctly link function definitions with calls at runtime based on the type of object pointer (base or derived) calling it.
A virtual table or vtable is essentially a table of all virtual functions and pointers to their respective definitions in the inheritance hierarchy. There also exists a vpointer that is a class member linked with the vtable.
Vtables are completely defined only after the constructor call is completed and any call to virtual functions done in the construtor initializer list will be ambigous and can crash the program.
Polymorphism in C++ explains vtables with better examples and in-depth context.
cron jobs December 9, 2019
A cron job is a sofware utility to schedule tasks by the clock and save repetitive manual runs. Cron jobs can be used to setup shell scripts or commands for system maintenance, data handling, emails, automated cache handling and many more mundane tasks.
A crontab is a special cron file with all commands and jobs and related instructions to be automated. A cron daemon is only started at boot and usually never automatically restarted thereafter.
crontab -e is the command used to edit the crontab configuration file. It provides standard options for scheduling the job by the minute, hour, day, month and day of the week. The cron job configuration also needs the exact command to be executed
This command runs the user-defined shell script at the beginning of each hour and could be as simple as setting a reminder to drink water!
0 * * * * /home/cron_job_script/execute.sh
friend in C++ November 18, 2019
A friend class in C++ can access the private and protected member variables of a different class. The friend class just needs to be declared in the concerned different class. Similarly, a friend method in C++ can access either protected/private methods or even global methods and use them within the class they are declared in.
A friend can be declared as private or protected or public in the class while the behavior remains unaffected. Friend behavior is neither mutual nor can be inherited. It only establishes access from the class declared in to the class being declared.
However, friend methods or variables should not be used extensively unless necessary as it defies the purpose of encapsulation in OOP. At the same time, it limits the extent of interaction permitted between two classes.
Declarations:
friend class Alpha;
friend int Alpha::search();
dpkg November 17, 2019
dpkg is a package manager for Debian-based systems(Linux-based open source softwares). It is a low level tool which can only install and uninstall packages asked explicitly. It is not intelligent enough to run automatic updates or manage dependencies. dpkg is very simple to use and useful for terminal based interaction with packages. Advanced Package Tool( apt) is the command line tool that uses dpkg as the backend. It is advanced in the sense that it can find the dependencies of the package being installed and uses dpkg to install them automatically, as well.
The -i argument is used to install packages, either from compressed zip files or .deb
For example: dpkg -i <software.>deb
The Ubuntu Help Website provides very comprehensive information about dpkg and more command line options can be looked up using man dpkg command.
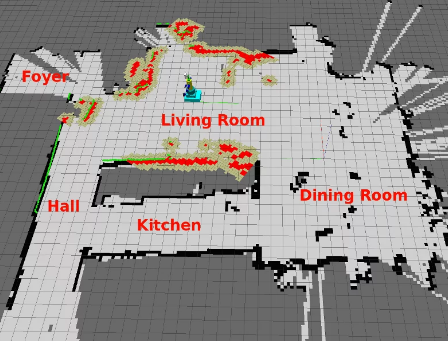 Simultaneous Localization & Mapping
Simultaneous Localization & Mapping